As companies explore outsourcing opportunities—whether for cost savings, efficiency gains, or access to specialized expertise—questions often arise about the broader social and economic consequences of these decisions. Outsourcing and income inequality is a particularly charged topic, especially in the United States, where shifting labor market dynamics, wage disparities, and global competitive pressures have sparked intense debates.
While some view outsourcing as a catalyst for innovation and productivity, others argue it contributes to a growing income divide by relocating certain jobs offshore, replacing stable positions with contract roles, or exacerbating wage stagnation in affected industries. Understanding these nuanced perspectives helps businesses navigate ethical considerations, align their strategies with corporate social responsibility goals, and make well-informed decisions that consider both economic outcomes and human impacts.
To contextualize these debates, revisit the Outsourcing Knowledge Hub: Definitions, Categories, and Industry Landscape for foundational insights. For a closer look at related operational considerations, see the HR Outsourcing Overview, which touches on workforce restructuring, or investigate how standards and best practices guide ethical outsourcing in National Outsourcing Association: Who Sets the Standards?.
The Outsourcing-Income Inequality Debate
In the United States, the discussion around outsourcing’s link to income inequality encompasses multiple factors:
Job Relocation and Offshoring:
When companies move manufacturing, customer service, or IT operations overseas, domestic workers may face layoffs, wage compression, or downward mobility. Critics argue that such shifts erode middle-class job opportunities, fueling economic polarization.Skill Polarization and Wage Gaps:
Outsourcing can disproportionately affect mid-skill positions while leaving high-skill knowledge work and low-wage service roles intact. This “barbell” effect may widen wage gaps, as high-paying jobs grow more exclusive and entry-level roles proliferate without upward mobility.Dynamic Market Forces:
Some economists emphasize that outsourcing is part of broader trends—globalization, automation, and policy choices—that influence the labor market. They argue that focusing solely on outsourcing oversimplifies the root causes of inequality.Efficiencies and Consumer Benefits:
Proponents note that outsourcing can lower costs, reduce consumer prices, and streamline operations, potentially boosting aggregate economic growth. In their view, these efficiency gains can lead to job creation in other sectors, offsetting some negative impacts.
Key Economic and Social Considerations
1. Wage Stagnation and Job Quality:
By shifting certain roles to regions with lower labor costs, companies may contribute to wage stagnation in the US for comparable positions. Over time, this can limit upward mobility and reduce bargaining power for workers, affecting both income levels and job quality.
2. Changing Labor Market Structure:
As certain production tasks move abroad, the domestic labor market may skew toward specialized, high-skilled positions in areas like R&D, management consulting, or software engineering. While these roles command premium wages, they are often accessible only to those with advanced education or in-demand skills, leaving less skilled workers at a disadvantage.
3. Regional Disparities:
Outsourcing’s impact is unevenly distributed. Regions heavily reliant on industries vulnerable to offshoring—such as manufacturing hubs in the Rust Belt—may experience higher unemployment, diminished property values, and reduced tax bases. These regional disparities can deepen income inequality across states and communities.
4. Supply Chains and Innovation:
Advocates for outsourcing argue that by improving cost structures and freeing capital, companies can invest in innovation, product development, and market expansion. Over time, such growth may generate new jobs, including high-value positions that help mitigate inequality. However, the timeline and extent of these benefits remain subjects of ongoing debate.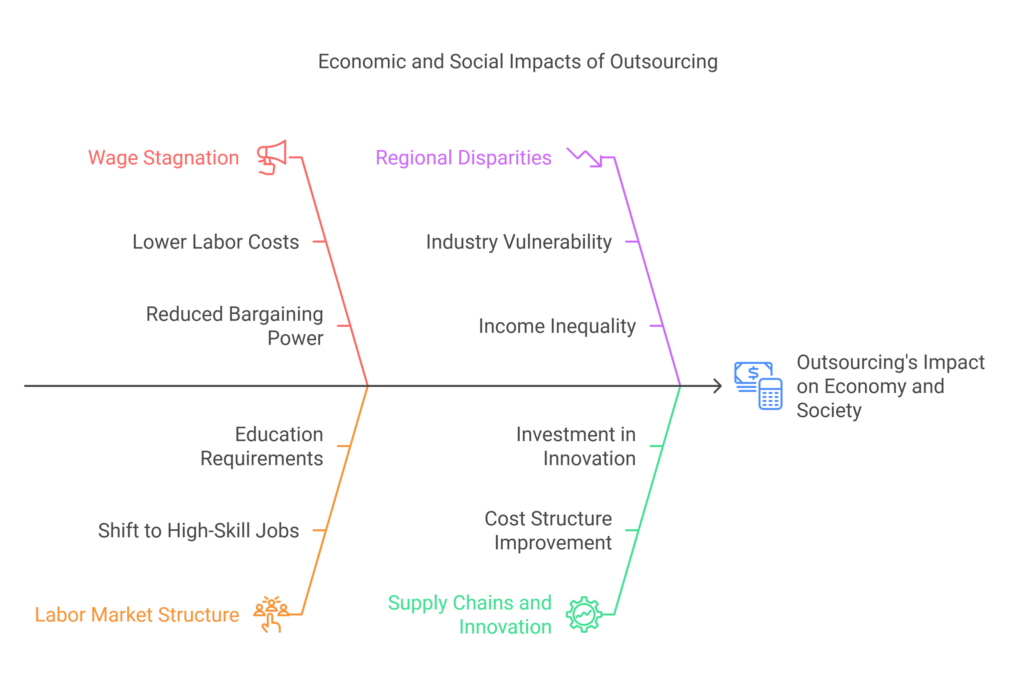
The Role of Policy and Corporate Strategy
Public policy and corporate decision-making both influence how outsourcing shapes income inequality:
Policy Interventions:
Government actions—such as job retraining programs, educational incentives, minimum wage adjustments, and tax policies—can soften the negative impacts of outsourcing. For example, workforce development initiatives help displaced workers acquire new skills, improving their prospects in a changing labor market.Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
Companies aware of these impacts may adopt CSR strategies to address inequality. This can include committing to domestic upskilling programs, investing in local communities affected by offshoring, or choosing outsourcing partners that maintain fair labor standards abroad.Ethical Vendor Selection:
Just as companies weigh quality and cost considerations, they can also assess prospective outsourcing vendors based on their labor practices, wage policies, and local economic impact. Aligning with National Outsourcing Association guidelines or similar standards ensures a baseline of responsible practice.
Evaluating Outsourcing’s Overall Impact
Determining outsourcing’s net effect on income inequality is complex. Studies vary in their conclusions, often depending on the metrics used and the industries examined:
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Perspectives:
Short-term analysis might highlight job losses and wage pressures, while long-term assessments consider whether market efficiencies eventually create different (and potentially higher-value) employment opportunities.Sector-Specific Dynamics:
Sectors like manufacturing, IT support, or call centers might experience varying degrees of wage and job polarization. Understanding these nuances helps firms predict outcomes more accurately.International Comparisons:
Looking at countries where outsourcing has been prevalent for decades can offer lessons. For instance, comparing the US experience with that of European nations may provide insights into how social safety nets, labor policies, and workforce training shape outcomes.
Informed Decision-Making and Ethical Outsourcing
For businesses, the question isn’t whether to outsource, but how to do so responsibly. By acknowledging the potential link between outsourcing and income inequality, companies can:
Prioritize Responsible Sourcing:
Opt for providers that value fair labor practices, skill development, and equitable wages, mitigating negative externalities.Invest in Domestic Workforce Development:
Offer training, reskilling, and career advancement paths to employees affected by outsourcing. Such investments may improve long-term worker loyalty, productivity, and brand reputation.Balance Cost Savings with Community Impact:
While cost efficiency remains a central outsourcing driver, businesses that also consider social implications can build goodwill, strengthen stakeholder relationships, and cultivate resilient markets.Engage in Dialogue and Transparency:
Communicate openly about outsourcing decisions with employees, local communities, and industry bodies. Transparency fosters trust and can help identify strategies that minimize adverse effects.
Conclusion: Navigating the Ethical Landscape of Outsourcing
Outsourcing and income inequality remain entwined in a complex debate. While outsourcing can produce cost efficiencies, spark innovation, and potentially bolster competitiveness, it may also exacerbate wage gaps, displace certain worker segments, and contribute to regional economic challenges. Understanding these dynamics equips businesses to make thoughtful, well-rounded decisions.

